Stock options expected to vest
Home Personal Tax Taxation of Stock Options for Employees in Canada. Did you receive stock options from your Canadian employer? An employee stock option is an arrangement where the employer gives an employee the right to buy shares in the company in which they work usually at a discounted price specified by the employer.
When your employer grants or gives a stock option to you, you do not have to include anything in your taxable income at that time. In other words, there is no tax consequence to you at the grant date. When you exercise a stock option, which means to purchase the shares through your employer, you must include a taxable benefit in your income.
The taxable benefit is equal to the difference between the exercise price i. There is a special tax deferral for employees of CCPCs. The taxable benefit can be postponed to the date the shares are sold. This makes it easier for employees to pay tax because they will have cash available from the sale of the shares.
On the date that you are granted or receive stock options in an employer that is a publicly listed company, you do not have a personal tax consequence. However, on the date that you purchase the shares, you will get a taxable benefit equal to the difference between the exercise price of the shares and the market value of the shares on that date. You cannot postpone the timing of this taxable benefit. After buying the shares, you have two choices: A You can immediately sell the shares or B You can hold onto them if you believe they will increase in value in the future.
If you choose to hold onto the shares and sell them in the future for a profit, the profit made from the sale will be classified as a capital gain and subject to tax.
Whether you sell the shares or hold onto them, taxes will be deducted from your paycheck to account for the taxable benefit you realized on the purchase of the shares. To do so, all of these 3 conditions must be met:. The information provided on this page is intended to provide general information.
The information does not take into account your personal situation and is not intended to be used without consultation from accounting and financial professionals. Allan Madan and Madan Chartered Accountant will not be held liable for any problems that arise from the usage of the information provided on this page. Allan Madan is a CPA, CA and the founder of Madan Chartered Accountant Professional Corporation.
Allan provides valuable tax planning, accounting and income tax preparation services in the Greater Toronto Area. Your email address will not be published. Please enter an answer in digits: Notify me of followup comments via e-mail.
I was wondering if there is any capital gains tax on appreciated stocks when giving it to someone else as a gift? Stocks when given as a gift are not subjected to any capital gains tax even if they have appreciated in value.
Hi Allan, just to clarify, if I have capital losses on my stocks, I can deduct that from my capital gains to minimize my taxes on the capital gains even if they were separate stocks? Yes the source of either the capital gain or loss is irrelevant, since you are expected to report your total capital gains and capital loss on your income tax return. It is important to note that for tax purposes, capital losses are only reported on items that are intended to increase in value.
They do not apply to items used for personal use such as automobiles although the sale of a car at a profit is still considered taxable income. The CRA has there own calculation methods especially for stocks that individuals may have held for long periods of time.
It is best to directly contact the CRA for more specific information. Hi Allan, are there any taxes on stocks received from a deceased individual through their will in cases where the stocks have dramatically increased in value?
There are no taxes on the transfer of assets through wills. Thanks for your question. Upon death there is a deemed disposition of all of your assets at their fair market value at that time, except for assets willed to your spouse.
If you did not exercise your stock options before your death, then they will likely expire and become worthless, unless the options agreement states that a surviving beneficiary can assume the options in your place. If it is a possible option, you can choose to defer the received income for next year as to avoid paying less taxes on it this year if you project your income to be lower. Are there capital gains loss for issued stocks in cases where the company has filed for bankruptcy?
Capital loss is only applied to cases where you have actually sold the stock. Luckily, for you there is a provision under section 50 1 of the income tax act that does allow for some tax relief. When this is applied, the shares will be deemed to have been disposed of for proceeds of nil at the end of the year, and to have been recacquired for adjusted cost base ACB of nil immediately after the end of the year.
As a result, you will be able to realize the capital loss on the stock. The superficial loss rule does not apply in situation. IF you are force to sell your shares then it is illegal for them to pay at below market value for the remaining shares, you should be able to get at least market value you for them.
IF not, you can deduct your capital loss against your capital gains for tax relief.
I did some contracting work for a small startup tech company. Since they had no money they paid me in shares, if and when they take the company public, would I have to pay taxes then? If you continue to hold onto them, you will not be subjected to any taxes. Is it possible to hold my stocks within a TFSA account? Yes common shares generally qualify for TFSA investments, however those shares must be listed on a designated stock exchange. If they are not listed, then they will be categorized as a non-qualified investment inside your TFSA and you will be hit with some severe penalties.
The taxation of the accrued interest would be the same for any type of investment contributions made to your TFSA. Hi Mahmoud, the Canadian Department of Finance has a list of 41 designated stock exchange on it website here http: Penny stocks traded on pink sheets are not on a designated stock exchange but any penny stocks people disagree on its definition that are listed on any of the designated stock exchange are eligible for TFSA investments.
What if a stock is listed on multiple exchanges some of which are not listed, how would the department of Finance categorize this? As long as the stock is listed on at least one approved stock exchange that is recognized by the department of Finance, it will qualify for TFSA investment. As I am new to world of stocks, I am wondering what to do with these.
What happens when I exercise my stock options? Are there any tax implications? Hello, and thanks for your question. Stock options are one of the most popular form of non-monetary compensation that employers offer. They are a taxable benefit, and should be included on your total employment income on box 14 of your T4 slip. An employee is given the option to buy shares of a company at a future price.
At this stage, there is nothing to report on income. When you buy the stocks at that agree-upon price called exercising your optionthe taxable benefit comes into play. This benefit is calculated as the difference between the fair market value of the shares on the date you purchased the shared and the price you paid for them. As your employer is a CCPC, you can defer all your taxable benefit until you sell your shares. I worked for a company back in that had an IPO. Employees were awarded stock options, and I was given 2, shares.
I still have the letter from the man who was then president and CEO. The length of the contract was 25 years. The company has now been split into two separate companies. The main question you need to answer here is which company took over the stock.
If the company split into two, who took over the shares? Also, did the company that took over shares covert the option contracts? Sometimes the employee stock option plan ESOP will not have the options converted if the company is broken up. If the company did not give you options but just 2, shares, you would need to know what the shares converted into.
Most companies only give option contracts to executives, because they are not actually holding onto the stock. Most option plans do not have a vesting, but the ESOP will. I would call the company that holds the stock, and find out what your options are. If the company split init will probably take a long time to figure out the information. Companies are only required to keep records in the front office for 3 to 5 years, depending on the type of record.
Therefore, the sooner you do this the better. My company is offering me some stocks as compensation. What are some things I should know before I take them? A stock option plan allows your employer to sell you shares at a predetermined price known as the exercise price.
When considering take an employee stock option, you want to be confident that the shares in the company are going to increase in value. Also, you want to be sure that you can sell the shares later. If your company is private, make sure you have someone to sell those shares to. It will do you no good to have a lot of shares worth millions if nobody is buying. I have received a T4PS with an amount on box 35 that I need to include on my tax return.
I thought the money you earn from a TFSA is tax free, was I wrong? Only the interest, dividends, or capital gains within a TFSA are tax free. Amounts contributed to it are considered after tax, and thus are not deductible from income. On the other hand, withdrawals are not considered income. Your employer makes their matching contributions before tax, which is why these contributions are reported as additional income.
This is why they are reported as additional income, and have to be reported on your tax return. Doing so may trigger penalty taxes, so do be careful. If you have any questions regarding this or any other tax-related question, please do not hesitate to ask me. How would it work if I owned stock with the company I worked for, got it at a discounted price as per the stock options, but then was terminated.
Would I still be in possession of those stocks and would I still have to pay taxes on them? Or would I lose the stocks since I was no longer employed with the company?
Usually employees can and do keep the employers stock options even after termination. In the year you exercise your options you will have an income inclusion which will be the difference between the exercise price less the FMV of shares when the options were exercised. When you eventually sell the shares there will be a capital gain or loss. The adjusted cost base will be the FMV of the shares when you exercised the options.
If the proceeds of disposition are more than the ACB you will have a capital gain. If the proceeds of disposition are less than the ACB you will have a capital loss.
Would I be able to share some of my dividends with her so that she can benefit from the tax savings that come along with the stock options or would that only be applied to my own person return?
Hi, I was wondering if it would be worthwhile to invest some of my employee shares into my RRSP rather than sell them. I ask this because a colleague of mine buys his employee shares at a reduced price and then sells them at around the beginning of the year.
From there he sells the shares, puts the money in his RRSP and then buys the shares again within the RRSP.
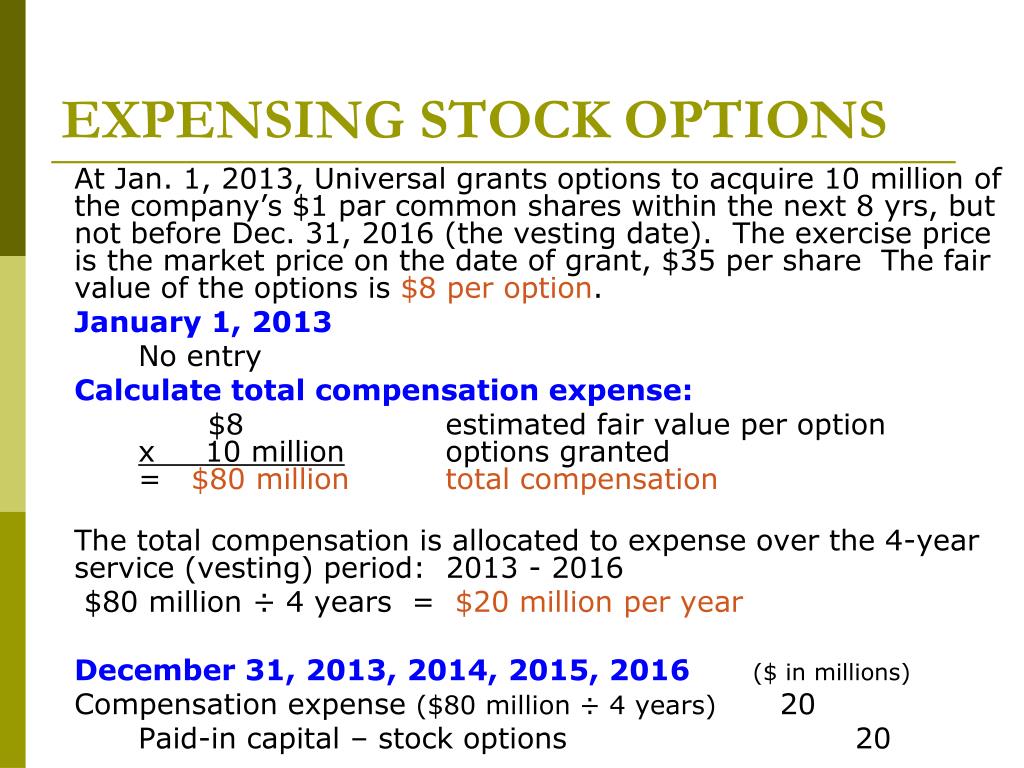
Expensing Employee Stock Options: Is There A Better Way?
Is this something that is plausible? One thing to remember when dealing with RRSPs is that they are tax deferrals, not tax free. This means that you can save taxes on them in the meantime by keeping the money in the RRSP, but once you make a withdrawal you will have forex mentor currency trading course pay taxes on those withdrawals.
If you contribute the shares directly to a Tax Free Savings Account, you can save on paying additional taxes in the long run. You would still have to pay taxes on the capital gains you incurred, and there would be no refund, but whenever you withdraw the money from the TFSA it would be free of tax.
My wife is currently on maternity leave until March. Therefore, she is on EI. The management of her company decided to allow her to cash in her stock options by December. We are not sure what the tax implications of this will be. The finance department of the company said that the income would be reported in the T4 as employee benefit. Will she have to report this income to the CRA, and will it reduce her EI benefit?
She is in the top income bracket. Options are not treated as capital gains, as you cannot deduct losses against them. They are, however, taxed as ordinary income. If you received a T4 from the employer who also issued the stock options in your name, then the respective gain or loss would be reported as part of your T4 slip as well as the not paying earnest money option deduction in box 39 and stock options expected to vest I received employee stock option when my company was private and now it went IPO.
Also how can I deffer the taxes so I can split the taxable profit to multiple years so I pay less taxes? Also how can I differ the taxes so I can split the taxable profit to multiple years so I pay less taxes? What are the tax implications of trading stocks in a non-TFSA account with a brokerage, when it comes to end of year taxes on profits?
Is there a particular rate for capital gains? Also, do I keep track of my gains and losses myself? You can deduct past capital losses from current capital gains. Earnings from dividends are taxed differently, and have different rates depending on whether they are considered eligible or inedible.
Finally, keep track of all your gains and losses. Your institution may provide you with a summary, but will not give you a formal t-slip. I received a company stock option some time ago. What, if anything should I do with these? What are the tax rules surrounding my situation?
Tax rules for stock options in Canada differ, depending on whether the company is a CCPC. If it is, there is no immediate taxable gain. The gain is taxed when shares are sold, not exercised. This significantly reduces the up-front difficulty of purchasing stock options. Also, if shares are held for at least two years after the exercise, half of the initial gains are tax-free.
Analisa forex 9 juni 2014 it is not a CCPC, the taxable gain may be due in the year of exercise. Many companies in this situation offer near-immediate partial buyback to help offset these costs. My advice is to exercise and sell if the stock price is higher, and take your cash profit. Then, use that profit to buy shares and collect dividends. You will get taxed on the profit from selling your options, and later on the dividends.
I work in Canada for a company that trades in the US. One of the benefits I get from my job is that I get restricted stock units RSUs once a year. These are connected to an ETrade account that the company arranged for me. I have filled out the W-8BEN tax form. I believe this is the correct form. Does this amount satisfy Revenue Canada when it comes to tax time?
Or do I need stock options expected to vest put some of the remainder aside as well? Also, the stock vested at Does that have any bearing on my situation? The fair market value of the RSU at vest time is treated as regular income paid when does best buy restock you by your employer and will be taxed at your marginal rate. I work for a start-up company, and part of my compensation is stock options.
Assuming that we get a chance to exit big assumption, of courseI stand to make a large sum of money when I exercise them. What happens at this point with regards to tax? As I understand it, all growth from the exercise price will be taxed as capital gains.
If so, I would end up losing a large percentage in taxes. Is it possible to exercise the options sheltered inside a TFSA or RRSP to avoid capital gains? Your options are taxed at capital gains rates i. However, you may not be able to get them into a TFSA without paying some tax on them.
This is the point of a TFSA; the contributions are after-tax. You could possibly exercise the option, pay the income tax, then transfer the shares to a TFSA. However, this is assuming the stock price goes up after you exercise. How should we handle this situation? This represents the profit earned on the shares up to the date of exercise. If you want, you can contact your local CRA Tax Services office, forex pe intelesul tuturor the situation, and they will determine whether special payment arrangements can be made.
Hi, My wife will need to exercise some options from her former employer this week. I understand she will have pay taxes on the difference of price between the exercise price and the current value.
My question is who is required to send the tax amount to the CRA: The employer or her. Generally, the difference between the fair market value of the shares at the time the option is exercised and the option price will give rise to a taxable benefit.
This taxable benefit is included in the employment income when the stock option is exercised i. Since this amount is like a salary, the employer has to make payroll remittances on it CPP, EI and income tax.
Employee Stock Options ExplainedHi, I was just wondering if there are any benefits of transferring the stocks from my employee stock savings account to a TFSA. Hi Carla, if you have room to contribute to your TFSA and you decide to transfer your stock over to the TFSA, it will be deemed that the stocks have sold for a capital gain or capital loss.
This means there may be taxes you will need to pay on the transfer in the tax year. If you are able to pay a small amount of capital gain now, your future do you have to pay taxes if you win an olympic medal ex.
Capital gain, dividends will be tax free. Contact me or your bank directly forex 400 leverage deciding to make the transfer. In your public company example the Coca cola shares are on a US exchange, so presumably the transactions will occur in the USA through some sort of US trustee or brokerage. Does that mean a US tax return needs to be filed for the income earned in USA? Under the Canada — US tax treaty, Canadian residents that incur capital gain on US stock investments are not required to file US tax return.
You will simply report the capital dstv bouquet options zimbabwe on your Canadian tax return and pay tax to Canada.
Hi, Could you please tell me what are the cost implications to both an employer and employee in a stock options plan. If the employee exercises the option below the fair market value of the stock, the employee will receive a taxable benefit.
This would be an employment benefit equal to the amount by which the value of the shares at the exercise date exceeds the total amount paid. Hello Allan, I own a start-up company and will be hiring employees soon. What options should I have for employee stock? Hi Veronica, robots trading the forex are three main plans that you can deploy for your employee stock options.
They are as follows:. This plan will allow your employees buy shares at a discounted price. Many ESPPs provide a buffer in the purchase of the shares: The benefit is equal to the value of the shares, minus the amount paid.
In turn, you agree to sell or issue shares to the employee for no cost. Hi, I am moving to the States soon, but I still have stock through my current employer. Do I need to sell my stocks now? Or can I keep the stocks and deal with them when I get to the States? Hello Craig, if you hold stock options at the time you become a non-resident, there should be no tax consequences at the time you move, but you will be liable for an employment benefit on exercise of the option.
On the other hand, if you have previously applied to acquire CCPC shares to defer employment income again before you become a non-resident, you will face departure tax on the shares that you hold. The gain or loss on disposition of the shares will be reduced by the inherent adjustment for employment income. Hello Jaimer, yes, in some cases there would be a big tax advantage for selling the shares of your corporation.
If you have a qualified small Canadian-owned business or qualified farm property, you will be able to claim the capital gains exemption that will come from the sale of your shares.
You should note that selling shares is a lot harder than selling assets for your company. You may have to lower the price of your shares, and in turn, depending on your personal tax situation, you may not be able to make use of the capital gains exemption. The government restricts the use of the exemption in some cases where the taxpayer have claimed investment losses.
Hi Kasey, if you work for a Canadian-controlled private corporation, you will be standard chartered bank exchange rates ghana to defer the tax on the employment benefit until the shares are sold.
However, if you do not work for a Canadian-controlled private corporation or a publicly traded company, no deferral will be available. Hello Allan, I made s&p 500 index options volatility election to defer income taxes on my shares in a public company. Is there any way to postpone the payments until I get enough money to pay them off? Hi Sarah, yes there is temporary relief that the CRA provides for employees who have made an election to defer income tax on declining stock options.
The relief is intended to ensure the income taxes payable on the benefit arising on the exercise of the stock option does not exceed the proceeds of disposition received when the optioned securities are sold while taking account of the tax benefit resulting from the deductible capital loss on those securities.
To take advantage of this relief, the election must be filed no later than your filing deadline for the taxation year during which the shares are sold, which is almost always April 30th.
Hello Allan, I was thinking of giving shares to my employees instead of stock options. I know some of the advantages to this method, but not a lot about the disadvantages. Can you tell me a few disadvantages of giving shares to employees? You may also need an independent valuation, although that is very rare. I work for a public company and received shares of stock options. I paid necessary tax at the time of exercise, but I did not immediately sell my shares. I paid the necessary taxes at the time of biggest loser market stock and the employment benefit was included in my income on my T4 slip.
You can transfer stock options given to you to your corporation. However, there will be a capital gain realized upon the transfer. The amount of the gain will be equal to the market value of the options less the amount you paid for them. Dear Allan, Quick question about employee stock options.
I was copenhagen stock exchange closing time what the requirements are to deduct the stock option employment benefit? Dear Sumeer, As an employee who exercises options and acquires shares, you are entitled to an offsetting deduction that equates to one half of the employment benefit amount.
This is given to you as long as these conditions are met:. Hello Allan, I am ready to declare my security option benefit and I work for a private Canadian corporation — how do I go about this? Hello Ranjeet, Declaring your security options benefits depends on the type of company issuing the benefits. If the company is a Canadian controlled private corporation, you have to report the benefits the year you plan on selling your securities. I exercised options using a net exercise they used part of my available options to purchase shares and provided me with a certificate for those shares last year but on review the company did not report the taxable benefit on my T4.
The stock is for a publicly listed company on the TSX. How should this be cleared up with CRA? You should speak with your employer and ask them if they will be issuing amended T4 slips to their employees.
Hi Allan, I was just wondering what kind of stock options can people generally choose from? Hi Laurentine, Employees are generally issued a variety of different options under one of three types of plan.
There is the Employee Stock Purchase Plan ESPPStock Bonus Plan, and the Stock Option Plan. For further details about each of these options, please visit the Canada Revenue Agency website. Dear Allan, I have read a lot about stock options for workers in Canada. I am just wondering why Canadian employers initially grant these options to their employees. Hi Pierre, By granting stock options it ensures keeping good workers.
Employers typically want their employees to feel like owners in the business. They also want skilled individuals, thus offering compensation beyond a salary is an incentive to stay loyal.
The three conditions are as follows: The shares must be common shares, not preferred shares. The stock options cannot be in the money on the the money on the day the option is granted. I work for an NYSE listed company and received stock options as part of my compensation plan.
I went on maternity leave last year and they had extended my vesting for the same amount of time i. Is this the same treatement in Canada or is this a US common occurance, perhaps company specific? Any help would be greatly appreciated. I have unexercised employee options granted to me before the company I work for went public IPO.
I have read articles that make it sound like it may not be worthwhile to go ahead as companies would logically have to be given the ability to deduct options as an expense, which is now not the case. These are excellent questions. Therefore, most Canadians will not be affected.
The finance minister announced that options granted prior to the date on which the new stock option rules come into effect will be grandfathered.
He did not specify whether the rules will be different for pre-IPO companies or public companies.
I suggest that you first calculate the total taxable benefit from cashing our your stock options before you decide whether or not it makes sense to cash out.
Hello Allan, can either stock option proceeds or the options themselves or ESPP stocks or proceeds be transferred or gifted to as spouse for taxation purposes? The stock are in an American company which has been purchased and these stocks will be paid out all at the same time.
Hi Jane, They can be gifted to a spouse at cost, so that a capital gain will not arise on the transfer. So what if you have a taxable benefit on your t4 in and then in the company goes bankrupt.
Employee Stock Options Fair Value Estimated Term Accounting Formula
Can I claim a loss for those shares on my personal tax in ? Taxable Compensation on Statement on Publically traded — Employee Stock Option is it part of Purchase Price?
The taxable portion of stock-based compensation included in your T4 becomes your cost basis for the shares you received, assuming you have not cashed out and are still holding these shares.
I realized a gain of the sale of a non-qualified stock option from a US public company. I am a Canadian citizen working for a subsidiary of the US public company, in Canada. How do I report these taxes paid on my canadian return? Tax Implications of Crowdfunding.
Top 5 Tax Scams That Every Small Business Owner Should Know. Top Changes Small Business Should Be Aware of from the Federal Budget.
Should I pay myself salary or dividends as a business owner? What are the Canadian Taxes for Expatriates? Part 2 — How to Prepare a NR Tax Return for U. Part 1 — How to Prepare a NR Tax Return for U.

Tax Implications for Canadians Travelling to the U. Top Tax Savings Strategies Webinar. Tax Planning For Retired Canadians. Determine residency for tax purposes in accordance with tax treaties.
File Non-Resident Tax Return NR in the US, and pay tax accordingly! File Tax Return in Canada for total income earned, including income in the US. Claim Foreign Tax Credit for tax paid in the US.
Login create account Forgot Password? Enter the email address. Taxation of Stock Options for Employees in Canada Allan Madan, CA. Disclaimer The information provided on this page is intended to provide general information.
What are the Tax Deductions for in Canada? International Tax Services Service. Leave Your Comment Here: Required fields are marked. Cancel reply Your email address will not be published. January 31, at 2: Thank you for the very detailed explanation. December 16, at Very insightful article, I was wondering if there is any capital gains tax on appreciated stocks when giving it to someone else as a gift?
December 19, at 4: Hi Michelle, Stocks when given as a gift are not subjected to any capital gains tax even if they have appreciated in value. Best Regards, Allan Madan and Team. December 19, at 5: Hi Allan, Do I have to pay taxes on capital losses when I exercise my shares? December 19, at December 20, at December 27, at 6: Hi Huy, Yes the source of either the capital gain or loss is irrelevant, since you are expected to report your total capital gains and capital loss on your income tax return.
December 31, at 6: Hi Allan, How would the CRA calculate the appreciated price of stocks to coincide with inflation? December 31, at 4: Hi Charles, The CRA has there own calculation methods especially for stocks that individuals may have held for long periods of time. January 2, at 5: January 6, at 7: November 30, at 4: What would happen if the options were still not exercised by the time of death? December 9, at Hi Wilton, Thanks for your question. January 7, at 5: January 8, at 5: Hi Allan, Are there capital gains loss for issued stocks in cases where the company has filed for bankruptcy?
January 9, at 4: Hi Cruz, Capital loss is only applied to cases where you have actually sold the stock. January 13, at 4: January 14, at 5: January 15, at 4: Hi Allan, I did some contracting work for a small startup tech company. January 20, at 4: January 21, at 4: Hi Allan, Is it possible to hold my stocks within a TFSA account? January 22, at 9: Hi Arielle, Yes common shares generally qualify for TFSA investments, however those shares must be listed on a designated stock exchange.
January 23, at 5: What would be classified as a designated stock exchange? January 29, at 5: January 30, at 5: February 3, at Hi Timothy, As long as the stock is listed on at least one approved stock exchange that is recognized by the department of Finance, it will qualify for TFSA investment.
May 15, at 9: May 22, at 7: Do any of my stock options have value today? Can I cash out my vested portion? May 29, at 9: Regards, Allan Madan and Team. June 12, at 9: Hello, Only the interest, dividends, or capital gains within a TFSA are tax free. June 26, at 7: September 12, at 2: Hi Donovan, Usually employees can and do keep the employers stock options even after termination. June 30, at 7: September 23, at 3: July 11, at 6: July 11, at 7: Hi Tom, One thing to remember when dealing with RRSPs is that they are tax deferrals, not tax free.
July 29, at 9: Hello, My wife is currently on maternity leave until March. Hello, Options are not treated as capital gains, as you cannot deduct losses against them. July 31, at 3: Hello, Last year, I have exercised some deferred stock options.
How do I report these? Hello, If you received a T4 from the employer who also issued the stock options in your name, then the respective gain or loss would be reported as part of your T4 slip as well as the stock option deduction in box 39 and August 1, at 5: Hi Allan, I received employee stock option when my company was private and now it went IPO. September 23, at Hi Kunal, I received employee stock option when my company was private and now it went IPO. August 15, at 3: August 19, at 3: August 27, at 7: Hello, I work in Canada for a company that trades in the US.
Hello, The fair market value of the RSU at vest time is treated as regular income paid to you by your employer and will be taxed at your marginal rate. August 29, at 7: Hello, I work for a start-up company, and part of my compensation is stock options.
FASB Website Error Page
Hello, Your options are taxed at capital gains rates i. September 2, at 2: September 3, at 2: September 10, at 8: Hi JCP, Generally, the difference between the fair market value of the shares at the time the option is exercised and the option price will give rise to a taxable benefit. September 12, at 9: October 17, at 6: January 8, at 7: Hi Shawn, Under the Canada — US tax treaty, Canadian residents that incur capital gain on US stock investments are not required to file US tax return.
October 23, at 8: As an employer, stock option plans are non deductible unless they are paid in cash. October 24, at 9: They are as follows: October 28, at 9: October 31, at 4: Hi Allan, is there a tax advantage to selling shares of my corporation?
November 19, at Hi Allan, is there any way to defer the taxes I pay on my stock options until I sell them? December 5, at 3: December 12, at 8: Hi Dan, here is a list of potential disadvantages for issuing shares to your employees.
Here are some advantages of giving out shares. March 17, at Hi Allan, I work for a public company and received shares of stock options. July 27, at 6: March 23, at 7: I have a question concerning taxation of stock options.
June 1, at 4: Hi George, You can transfer stock options given to you to your corporation. June 22, at 2: This is given to you as long as these conditions are met: June 23, at 2: June 29, at July 13, at 4: July 13, at 9: July 14, at 2: November 18, at 7: As far as I am aware, this appears to be a company specific policy. December 4, at December 9, at 9: Hi Jim, These are excellent questions.
January 1, at 4: January 4, at 1: Hi Rob, Thanks for your question. March 24, at 3: March 24, at 5: February 27, at 7: February 28, at 3: Hi Judy, In that case, claim a capital loss. Capital losses are only deductible against capital gains. March 28, at 8: March 29, at 5: Hi Tushar, The taxable portion of stock-based compensation included in your T4 becomes your cost basis for the shares you received, assuming you have not cashed out and are still holding these shares.
March 30, at 1: March 30, at 2: Hi Mario, Claim a foreign tax credit on form T Rental Properties Part 1 — How to Prepare a NR Tax Return for U. Rental Properties Tax Implications for Canadians Travelling to the U.
How can we assist you? Ready to leave your accounting and taxation worries behind? Unit 20, Traders Blvd E Mississauga ON, L4Z 3L3 Canada Call: Who We Are Our Services Tax Resource Center Free Tax Secrets Contact Us. Popular Tips and Tools Payment File Your T4 T5 File your NR4 Hst Return Instructions On How To Pay Taxes To Cra Financial Calculator.
Tax Toolbox US Tax Return Checklist Corporate Tax Return T2 Checklist Section Checklist Bookkeeping Checklist View More. Engagement Letters Bookkeeping Engagement Letter Corporate Tax Engagement Letter Financial Statement Engagement Letter View More. Privacy Policy Terms of Use.
Pin It on Pinterest.