Cross currency basis swap definition
Currency swaps are motivated by comparative advantage. Currency swaps are over-the-counter OTC derivatives. Additionally, cross-currency swaps are an integral component in modern financial markets as they are the bridge needed for assessment of yields on a standardised USD basis.
For this reason there are also used as the construction tool in creating collateralized discount curves for valuing a future cashflow in a given currency but collateralized with another currency. Given the importance of collateral to the financial system at large, cross-currency swaps are important as a hedging instrument to insure against material collateral mismatches and devaluation,.
For instance, a US-based company needing to borrow Swiss francs, and a Swiss-based company needing to borrow a similar present value in US dollars, could both reduce their exposure to exchange rate fluctuations by arranging either of the following:.
Also, suppose that the Piper Shoe Company, a U. To meet each other's needs, suppose that both companies go to a swap bank that sets up the following agreements:.
Piper Company to finance the construction of its British distribution center. The British company, with its U. The American company, with its British asset distribution center , will pay the 7. In a floating-for-floating cross currency swap, the interest rate on both legs are floating rates.
Such swaps are also called cross currency basis swap. In a fixed-for-floating cross currency swap, the interest rate on one leg is floating, and the interest rate on the other leg is fixed. Such swaps are usually used for a minor currency against USD. In a regular cross currency, the notional amounts of both legs are constant during the life of the swap. However, in a mark-to-market cross currency swap , the notional amount of one of the legs is subject to adjustment while the notional amount of the other leg remains constant.
The market-to-market variation is paid or received. Non-deliverable CCS, usually abbreviated as NDCCS or simply NDS , are very similar to a regular CCS, except that payments in one of the currencies are settled in another currency using the prevailing FX spot rate.
NDS are usually used in emerging markets where the currency is thinly traded, subject to exchange restrictions, or even non-convertible.
It is well recognized [8] [9] that traditional "textbook" theory does not price cross currency basis swaps correctly, because it assumes the funding cost in each currency to be equal to its floating rate, thus always giving a zero cross currency spread. This is clearly contrary to what is observed in the market. In reality, market participants have different levels of access to funds in different currencies and therefore their funding costs are not always equal to LIBOR.
An approach to work around this is to select one currency as the funding currency e.
BNP Paribas GlobalMarkets
USD , and select one curve in this currency as the discount curve e. USD interest rate swap curve against 3M LIBOR. Cashflows in the funding currency are discounted on this curve. Cashflows in any other currency are first swapped into the funding currency via a cross currency swap and then discounted. In the s Goldman Sachs and other US banks offered Mexico, currency swaps and loans using Mexican oil reserves as collateral and as a means of payment. In May , Charles Munger of Berkshire Hathaway Inc.
Currency swaps were originally conceived in the s to circumvent foreign exchange controls in the United Kingdom. At that time, UK companies had to pay a premium to borrow in US Dollars.
To avoid this, UK companies set up back-to-back loan agreements with US companies wishing to borrow Sterling. The concept of the interest rate swap was developed by the Citicorp International Swap unit but cross-currency interest rate swaps were introduced by the World Bank in to obtain Swiss francs and German marks by exchanging cash flows with IBM. During the global financial crisis of , the currency swap transaction structure was used by the United States Federal Reserve System to establish central bank liquidity swaps.
The aim of central bank liquidity swaps is "to provide liquidity in U.
The People's Republic of China has multiple year currency swap agreements of the Renminbi with Argentina , Belarus , Brazil , Hong Kong , Iceland , Indonesia , Malaysia , Singapore , South Korea , United Kingdom and Uzbekistan that perform a similar function to central bank liquidity swaps. The two nations can exchange up to The three-year currency swap could be renewed if both sides agree at the time of expiration. It is anticipated to promote bilateral trade and strengthen financial cooperation for the economic development of the two countries.
The basic mechanics of FX swaps and cross-currency basis swaps
The arrangement also ensures the settlement of trade in local currency between the two countries even in times of financial stress to support regional financial stability. From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. Not to be confused with Foreign exchange swap. Development Bank of Japan. CARF Working Paper Series No. Credit spread Debit spread Exercise Expiration Moneyness Open interest Pin risk Risk-free interest rate Strike price the Greeks Volatility. Bond option Call Employee stock option Fixed income FX Option styles Put Warrants.
Asian Barrier Basket Binary Chooser Cliquet Commodore Compound Forward start Interest rate Lookback Mountain range Rainbow Swaption. Collar Covered call Fence Iron butterfly Iron condor Straddle Strangle Protective put Risk reversal. Back Bear Box Bull Butterfly Calendar Diagonal Intermarket Ratio Vertical. Binomial Black Black—Scholes model Finite difference Garman-Kohlhagen Margrabe's formula Put—call parity Simulation Real options valuation Trinomial Vanna—Volga pricing.
Amortising Asset Basis Conditional variance Constant maturity Correlation Credit default Currency Dividend Equity Forex Inflation Interest rate Overnight indexed Total return Variance Volatility Year-on-Year Inflation-Indexed Zero-Coupon Inflation-Indexed.
Authorization denied
Contango Currency future Dividend future Forward market Forward price Forwards pricing Forward rate Futures pricing Interest rate future Margin Normal backwardation Single-stock futures Slippage Stock market index future. Energy derivative Freight derivative Inflation derivative Property derivative Weather derivative.
Collateralized debt obligation CDO Constant proportion portfolio insurance Contract for difference Credit-linked note CLN Credit default option Credit derivative Equity-linked note ELN Equity derivative Foreign exchange derivative Fund derivative Interest rate derivative Mortgage-backed security Power reverse dual-currency note PRDC.
Consumer debt Corporate debt Government debt Great Recession Municipal debt Tax policy.
Retrieved from " https: Foreign exchange market Derivatives finance. Navigation menu Personal tools Not logged in Talk Contributions Create account Log in. Views Read Edit View history. Navigation Main page Contents Featured content Current events Random article Donate to Wikipedia Wikipedia store. Interaction Help About Wikipedia Community portal Recent changes Contact page. Tools What links here Related changes Upload file Special pages Permanent link Page information Wikidata item Cite this page.
This page was last edited on 3 June , at Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License ; additional terms may apply.
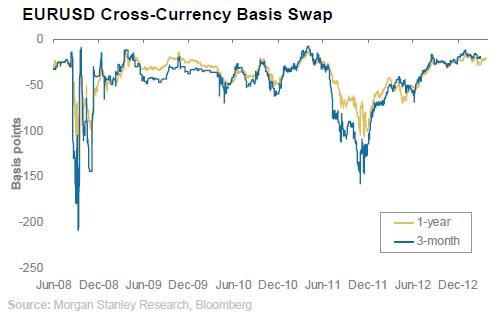
The cross-currency basis blowout and what it means for the USD
By using this site, you agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy. Privacy policy About Wikipedia Disclaimers Contact Wikipedia Developers Cookie statement Mobile view. Currency band Exchange rate Exchange-rate regime Exchange-rate flexibility Dollarization Fixed exchange rate Floating exchange rate Linked exchange rate Managed float regime.
Foreign exchange market Futures exchange Retail foreign exchange trading. Currency Currency future Currency forward Non-deliverable forward Foreign exchange swap Currency swap Foreign exchange option.
Bretton Woods Conference Smithsonian Agreement Plaza Accord Louvre Accord. Bureau de change Hard currency Currency pair Foreign exchange fraud Currency intervention. Terms Credit spread Debit spread Exercise Expiration Moneyness Open interest Pin risk Risk-free interest rate Strike price the Greeks Volatility.